Your Time has Finished
Which UCAT Exam
are you sitting?
Loading...
AR Shape Patterns
Your Score:
Average Score of All Users:
You performed better than of students
Section Breakdown
| Your Score | Average of all Users | Percentile | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape Patterns |
Shape Patterns
Your score:
Average score:
You performed better than of students
Abstract Reasoning Practice Subtest Instructions
There are 4 different question types in this section of the exam.
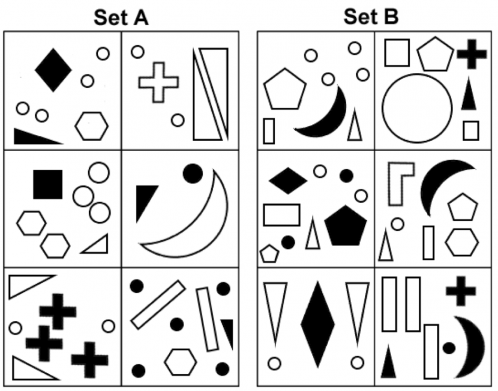
For type 1, you will be presented with two sets of shapes labelled “Set A” and “Set B”. You will be given a test shape and asked to decide whether the test shape belongs to Set A, Set B, or Neither.
For type 2, you will be presented with a series of shapes. You will be asked to select the next shape in series.
For type 3, you will be presented with a statement, involving a group of shapes. You will be asked to determine which shape completes the statement.
For type 4, you will be presented with two sets of shapes labelled “Set A” and “Set B”. You will be asked to select which of the four response options belongs to Set A or Set B.
It is in your best interest to answer all questions as there is no penalty for guessing. All unanswered questions will be scored as incorrect.
Click the Next (N) button to proceed.
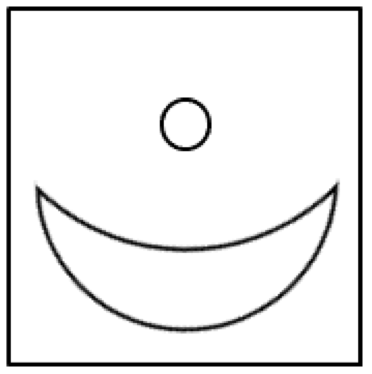
Explanation
Set C – This has a circle but no triangle, either right-angled or isosceles.
Pattern: Members of Set A contain at least one right-angled triangle and at least one circle; members of Set B contain at least one isosceles triangle and at least one circle.
Method: This is hard to spot, and so a process of elimination may help. There aren’t enough obviously-large shapes for Size to be a factor, nor does Orientation or Position vary in a clear pattern. Counting the number of shapes in the simplest cases (middle-right for A, bottom-left for B) enables exclusion of pure Number, whilst Colour is also easily checked and dismissed. Focussing on the shapes in these simplest cases (top- and middle-right for A, bottom-left for B) should reveal the importance of circles and triangles.